
Pre/ Post Gallery in Lacey, WA Dermatology Clinic for Animals
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats. It is also the most common variant of pemphigus diseases,1,2 which are characterized by autoantibodies that target keratinocyte desmosomal proteins, leading to loss of cell-to-cell adhesion (acantholysis).

How to Recognize Autoimmune Skin Disease Tips for Spotting Pemphigus Foliaceus
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats. It is also the most common variant of pemphigus diseases,1,2 which are characterized by autoantibodies that target keratinocyte desmosomal proteins, leading to loss of cell-to-cell adhesion (acantholysis). Acantholysis of keratinocytes causes separation and.

How to Recognize Autoimmune Skin Disease Tips for Spotting Pemphigus Foliaceus
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common form of the pemphigus complex in small animals and the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs.1,2 This review aims to provide an update on the pathogenesis of pemphigus foliaceus, as well as its clinical manifestations, diagnosis and therapeutic approach. Pathogenesis. Clinical signs.
Generalized pemphigus foliaceus dog
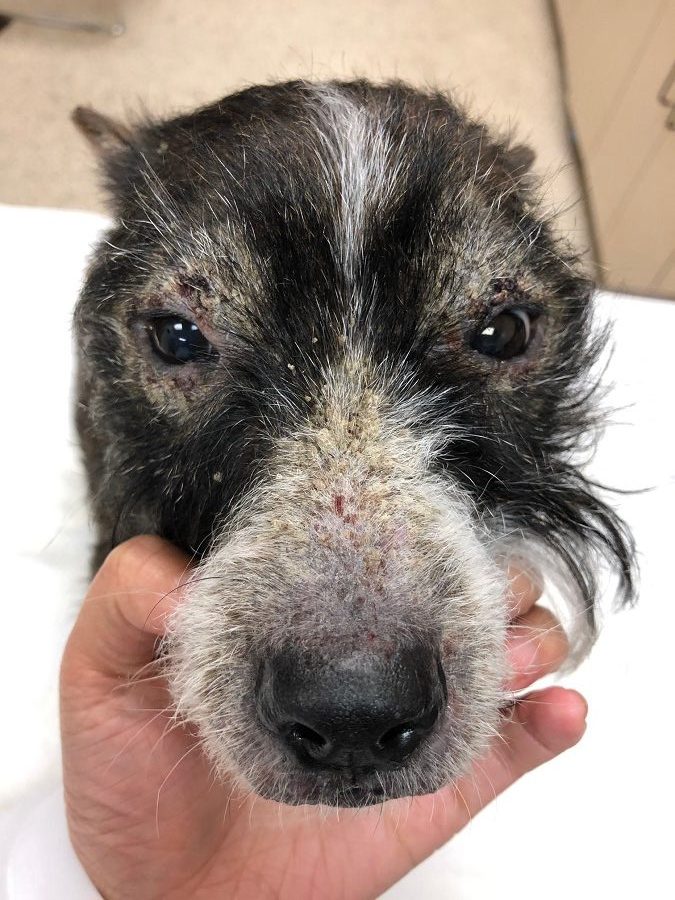
Pemphigus Foliaceus - Pemphigus foliaceus is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats. It is often observed in middle-aged and older patients. Pemphigus foliaceus typically causes hair loss, scabs, and ulcers (open sores) around the head, face and ears.

Disease facts pemphigus foliaceus in the dog and cat Companion Animal
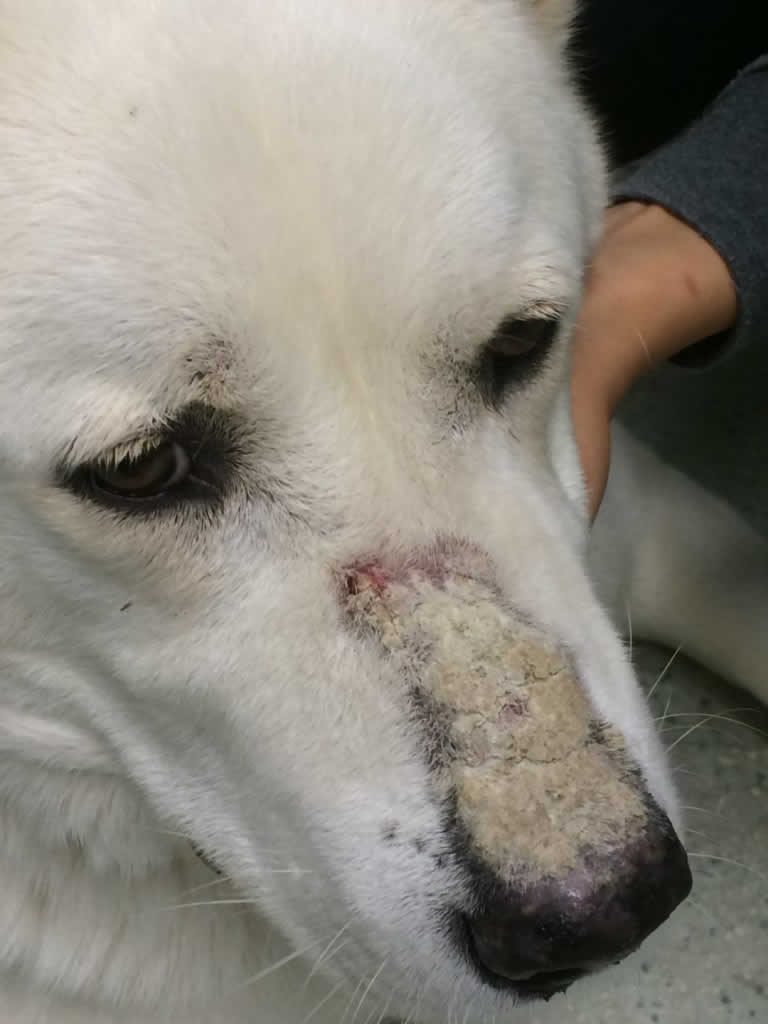
Pemphigus foliaceus is a severe skin disease that is characterized by pustules and blisters that rupture, causing damage to the skin of the face, ears, feet and eventually the entire skin in dogs. Pemphigus Foliaceus in dogs is commonly shortened and referred to as just "Pemphigus". This disease results when the animal recognizes a specific.
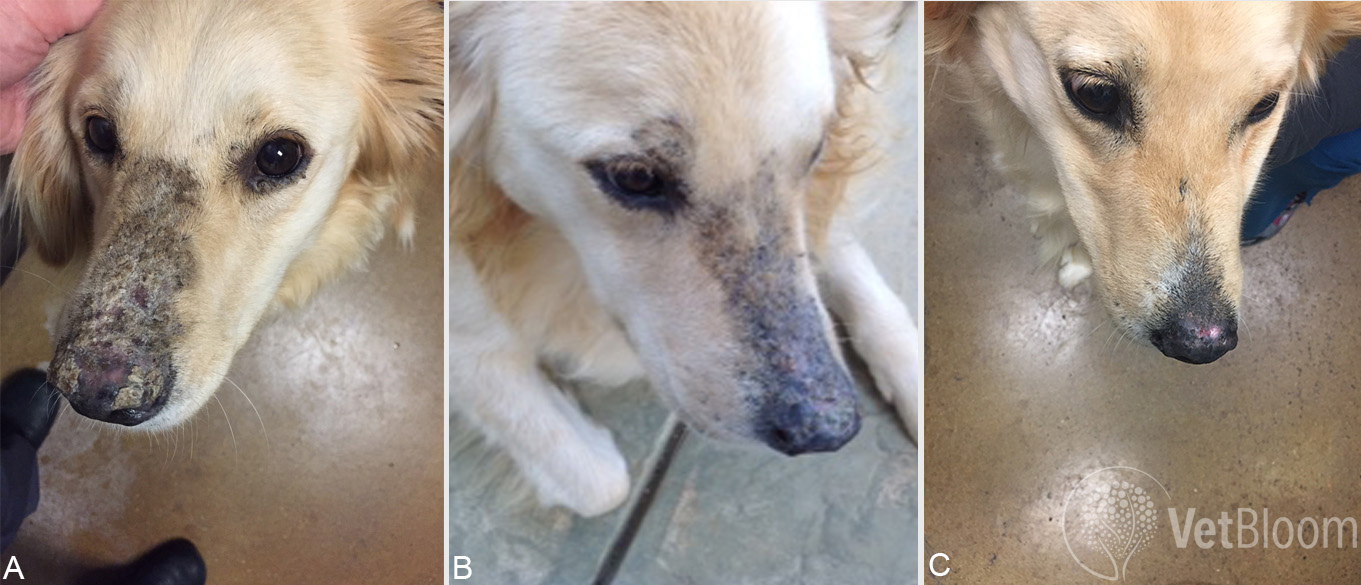

Pemphigus foliaceus VetBloom blog
Pemphigus is a potentially life-threatening, autoimmune blistering disease characterized by the presence of circulating antibodies against desmogleins, key components of the integrity of epidermal intercellular adhesion. However, in contrast to pemphigus vulgaris (PV) where mucosal lesions are classically present, pemphigus foliaceus (PF) there is only skin involvement without mucosal lesions.

Le pemphigus foliacé chez le chien et chez le chat Le Point Vétérinaire n° 233 du 01/03/2003
Pemphigus in dogs is an autoimmune condition of the skin. Pemphigus causes the connections between a dog's skin cells to break down.. Pemphigus foliaceus usually appears on the head, face, and ears with symmetrical lesions on both sides of the head. A dog's footpads are often affected as well. The trunk of their body is sometimes.
Pet Case Study Rocky’s Pemphigus Animal Dermatology Referral Clinic (ADRC)
Pemphigus in Dogs Estimated Reading Time: 4 minutes Pemphigus can best be described as an immune-mediated skin disease in dogs where a dog's own immune system begins to attack the connection between the normal layers of skin cells. There are different types of pemphigus that involve different areas of the skin.
Pemphigus Foliaceus The Skin Vet
Key words: Pemphigus, crusting, canine, auto-immune, dog Diagnosis and management of pemphigus foliaceus in dogs For Dermatology Referrals in your area: vetindex.co.uk/derm For Lab Tests and Equipment: vetindex.co.uk/Lab Market your referrals in VetIndex! For further information call us on 01225 445561 or e-mail: [email protected] Introduction.
Skin Veterinary Skin Specialist Veterinary Dermatology
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common autoimmune disease in dogs. It is characterized by pustules, ulcers and crusts (scabs) developing on the canine's skin surface. Symptoms of Pemphigus Foliaceus in Dogs Redness Blisters Pus Yellow-brown crust (scabs) Depression Lethargy Fever Sometimes itchy Hair loss Ulcers Lack of appetite
Pemphigus foliaceus Medisch Centrum Voor Dieren
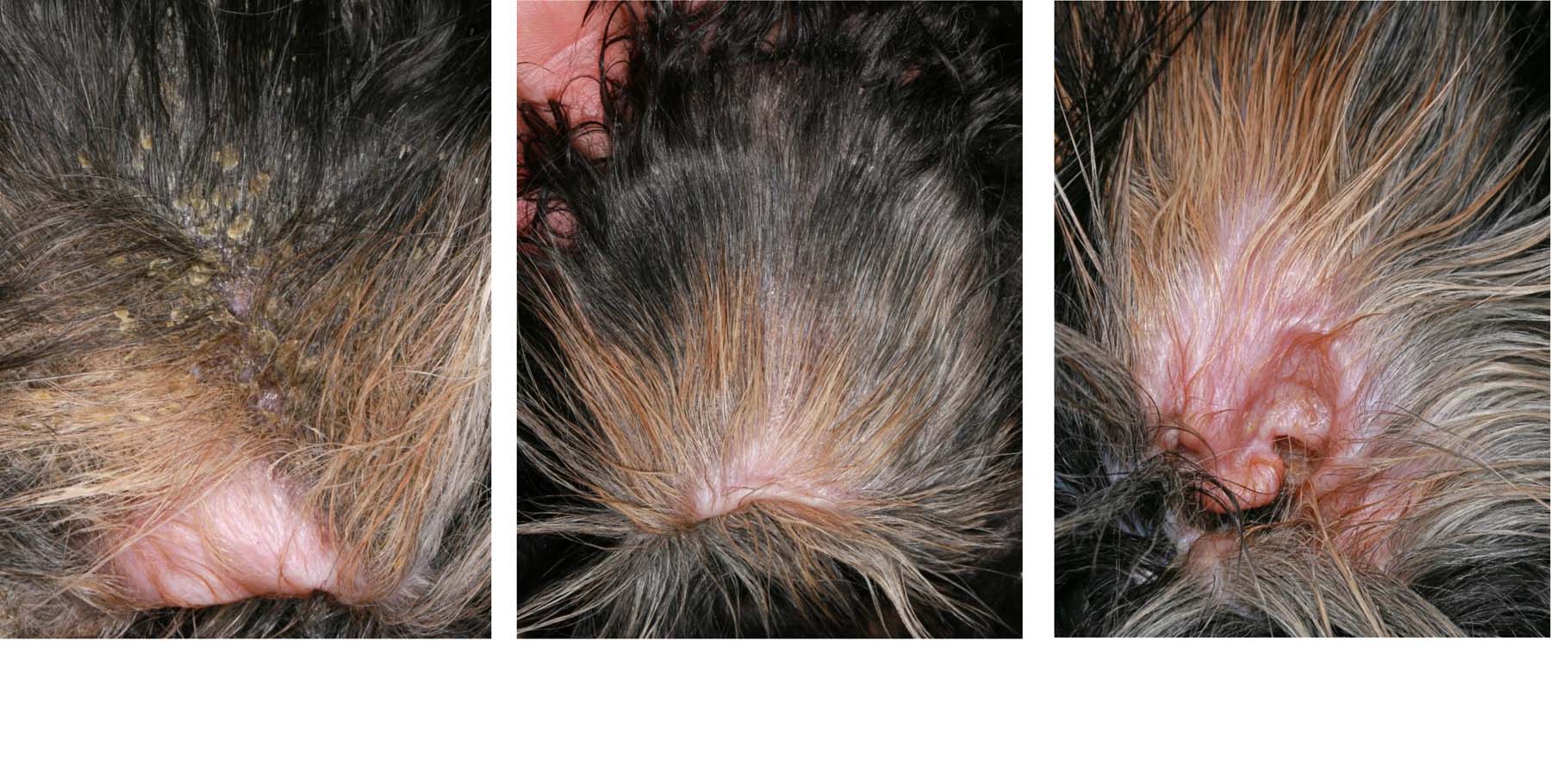
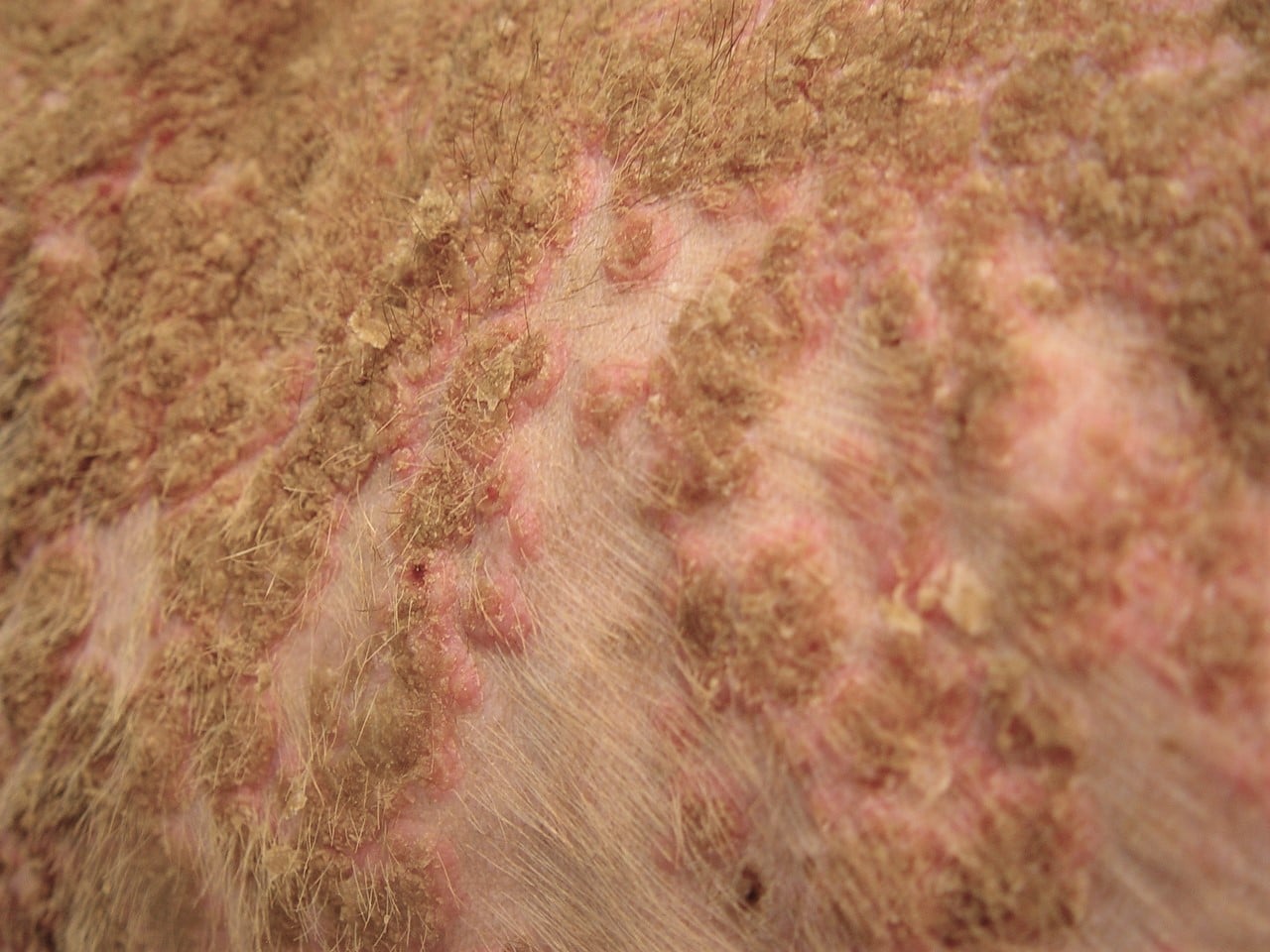
Pemphigus foliaceous is the most common autoimmune disease in dogs and is most often caused by autoantibodies targeting desmocollin-1 ( 2, 3 ). Go to: Clinical presentation The classical lesions of pemphigus foliaceous are large pustules that span multiple hair follicles ( 1, 4 ).
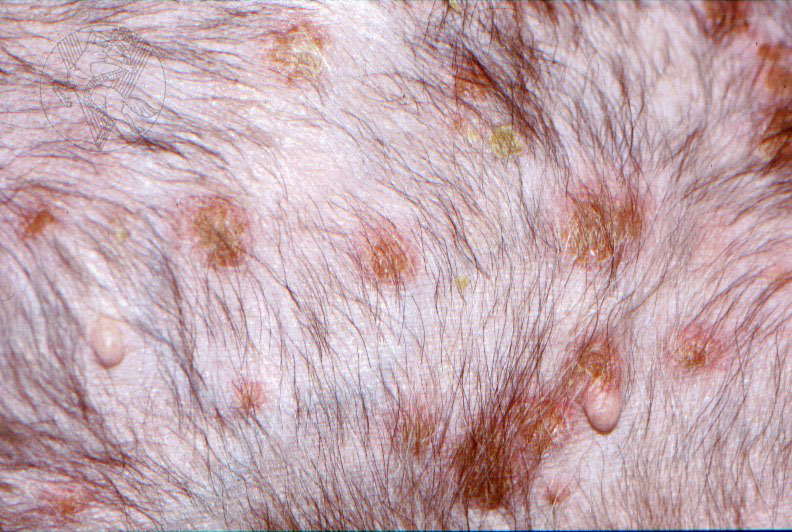
Generalized pemphigus foliaceus dog
Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus. Pemphigus foliaceus, the most common autoimmune dermatosis in dogs, presents with primary large, superficial pustules. Pustules may be punctate or span multiple follicles, and contents may appear translucent to yellow ( Figure 1). Because they are thin-roofed, pustules tend to rapidly rupture and form crusts with.

Pemphigus Foliaceus Dog
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is a type of autoimmune disease of the skin. Other skin diseases besides PF also have the word "pemphigus" in their name, but are different from PF. What Species or Breeds get Pemphigus Foliaceus? Although an uncommon skin disease in dogs and cats, any breed of dog or cat can develop PF.

TCVM for Treating Autoimmune Skin Diseases Today's Veterinary Practice
Bizikova P, Olivry T (2015) Oral glucocorticoid pulse therapy for induction of treatment of canine pemphigus foliaceus - a comparative study. Vet Derm 26, 354 PubMed. Bizikova P, Linder K E, Olivry T (2014) Fipronil-amitraz-S-methoprene-triggered pemphigus foliaceus in 21 dogs: clinical, histological and immunological characteristics.

A Retrospective Evaluation of the Treatment of Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus Veterinary 33
Pemphigus Foliaceus is an autoimmune vesicobullous to pustular skin disease in dogs characterized by acantholysis or loss of adhesion between keratinocytes within the epidermis and hair follicles. The disease is characterized by production of autoantibodies against intercellular connections of the keratinocytes.

Pemphigus foliaceus Stock Image C034/8791 Science Photo Library
Pemphigus foliaceus is the most common of these diseases, occurring more often in dogs than in cats and horses. It is characterized by the development of erosions, ulcerations, and thick encrustations of the skin and mucocutaneous junctions.